TTX has different binding affinities for different sodium channel isoforms. What does TTX do to voltage-gated Na channels.

Generalization To Sodium Channels A Structure Of Voltage Gated Na Download Scientific Diagram
If a nerve rather than an.

. Importance of Voltage-Gated Na Channels. How does the effect of lidocaine differ from the effect of TTX. Tetrodotoxin TTX is a natural inhibitor and blocks single sodium channels in.
Lidocaine also binds to the voltage-gated Na channels in the channels open state as well as its inactive state. Axon had been used in the lidocaine experiment the responses recorded at R1 and R2 would be the sum. What does TTX do to voltage-gated Na channels.
Lidocaine blocks the diffusion of Na through the voltage-gated Na channels. The importance of Voltage-Gated Na Channels 1. What does lidocaine do to voltage gated na channels Essays and Research Papers Page 1 of 50 - About 500 Essays The Action Potential.
How does the effect of lidocaine differ from the. On the other hand Castaneda-Castellanos et al. Local anesthetics antiarrhythmics and anticonvulsants include both charged and electroneutral compounds that block voltage-gated sodium channels.
Your answer. If lidocaine increases inward INa or stabilizes the open state of voltage-dependent sodium channels lidocaine is also expected to change Na i. Local anesthetic drugs interfere with excitation and conduction by action potentials in the nervous system and in the heart by blockade of the voltage-gated Na channel.
How does the effect of lidocaine differ from the effect of TTX. Its effect is different from TTX because it is usually used to block pain where as TTX is a poison. This causes depolarization as the membrane potential rises to 30mV.
However lidocaine is unable to bind in the resting state of the channels which is why it is used as an anesthetic in dental surgeries. 10reported that lidocaine 01 mm maintains the voltage-dependent sodium channels in an open state resulting in Na influx and neuronal excitability. TTX and lidocaine both block the diffusion of Na accross the channel.
Prior studies have revealed a common drug-binding region within the pore but details about the binding sites and mechanism of block remain unclear. Drug affinity varies with gating state of the channel. The effect of lidocaine is different from the effect of TTX because TTX is irreversible while the effect of lidocaine can be reversed.
A nerve is a bundle of axons and some nerves are less sensitive to lidocaine. TTX binding physically blocks the flow of sodium ions through the channel thereby preventing action potential AP generation and propagation. Lidocaine is slow at reacting and eventually wears off.
Lidocaine interacting with a sodium channel. The local anaesthetic works by moving to the inside of the cell then binding to the sodium channel and so blocking the influx of sodium ions. How does the effect of lidocaine differ from the effect of TTX.
Lidocaine blocks the voltage-gated sodium channels keeping sodium ions from entering. TTX on the other hand irreversibly binds to. Lidocaine is not always sensitive to the receptors and TTX causes irreversible damage.
What does lidocaine do to voltage-gated Na channels. Thus depolarization elicited by sensory stimulation generator or receptor potentials does not lead to the generation of action potentials that can travel to the central nervous system. Lidocaine blocks the diffusion of Na through voltage-gated Na channels.
Unline TTX the effects of lidocaine are reversible. Local anesthetics such as lidocaine Xylocaine and procaine Novacaine prevent the generation of action potentials by inhibiting voltage-gated Na channels of sensory neurons. What does lidocaine do to voltage-gated Na channels.
This protein folds into a cylindrical shape with a central channel that can be opened and closed in response to voltage signals from the nerve cell. If a nerve rather than an axon had been used in the lidocaine. A nerve is a bundle of axons and some nerves are less sensitive to lidocaine.
What does lidocaine do to voltage-gated Na channels. The drugs show low affinity at. It is slower at closing the gates A nerve is a bundle of axons and some nerves are less sensitive to lidocaine.
Lidocaine binds to voltage-gated sodium channels in a 1. At this time the voltage gated Na channels enter the inactivated state and Na stops entering the cell. Mutagenesis experiments have identified multiple residues lining the pore that are important in the lidocaine block Nau Wang 2004 and molecular models have been developed to account for how lidocaine binds to these residues.
Lidocaine blocks the diffusion of sodium through the voltage-gated sodium channels. A nerve is a bundle of axons and some nerves are less sensitive to lidocaine. Tetrodotoxin TTX is a potent toxin that specifically binds to voltage gated sodium channels.
What does TTX do to voltage -gated sodium channels. For example if the voltage gated Na channel is blocked the cell will not be able to depolarize and the action potential will not be generated. 1 fashion and prevents the flow of sodium ions through the channel pore.
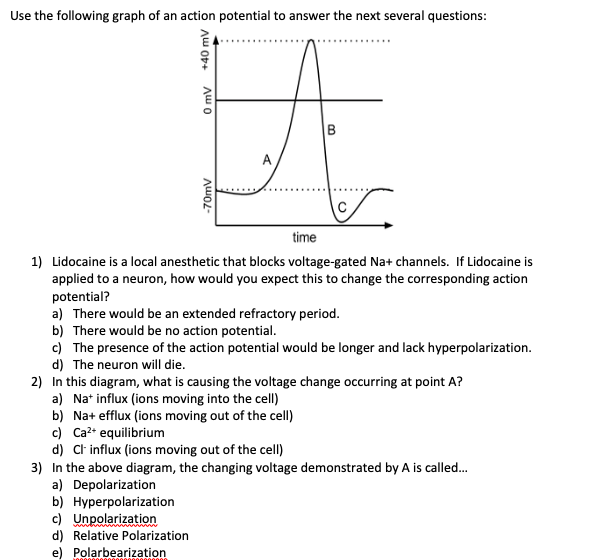
Solved Use The Following Graph Of An Action Potential To Chegg Com

The Effect Of Lidocaine On The On The Voltage Dependent Fl Uorescence Download Scientific Diagram
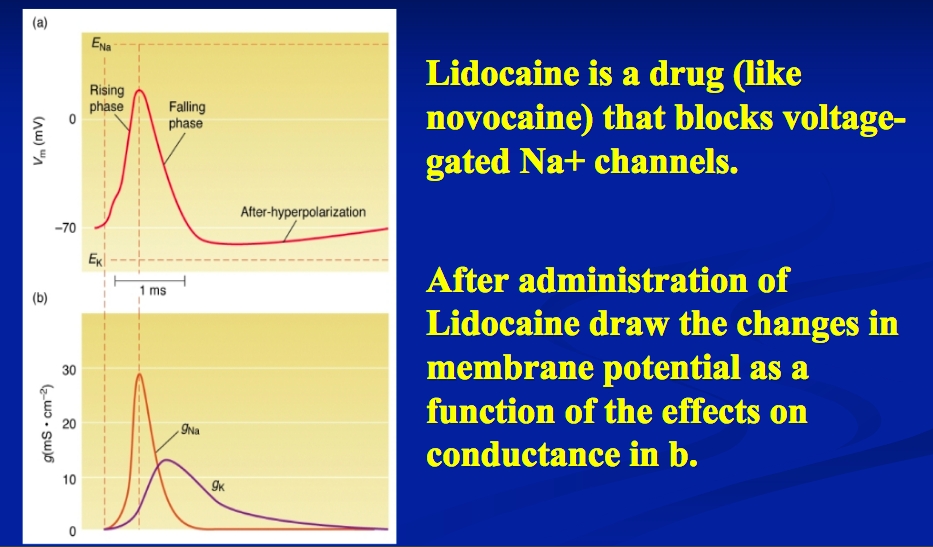
0 Comments